hwasan源码探究
llvm版本:cd4c10afea7eaaf87c1830e340863f0bf8745b0b
直接在llvm官网找到github链接clone就可以了。
常用函数
user内存和影子内存的转换,非常好理解:
//compiler-rt/lib/hwasan/hwasan_mapping.h
inline uptr GetShadowOffset() {
return SANITIZER_FUCHSIA ? 0 : __hwasan_shadow_memory_dynamic_address;
}
inline uptr MemToShadow(uptr untagged_addr) {
return (untagged_addr >> kShadowScale) + GetShadowOffset();
}
inline uptr ShadowToMem(uptr shadow_addr) {
return (shadow_addr - GetShadowOffset()) << kShadowScale;
}
inline uptr MemToShadowSize(uptr size) {
return size >> kShadowScale;
}
bool MemIsApp(uptr p);
inline bool MemIsShadow(uptr p) {
return (kLowShadowStart <= p && p <= kLowShadowEnd) ||
(kHighShadowStart <= p && p <= kHighShadowEnd);
}堆分配记录
每个线程都有线程本地变量,记录每个分配。
static void HwasanDeallocate(StackTrace *stack, void *tagged_ptr) {
CHECK(tagged_ptr);
void *untagged_ptr = UntagPtr(tagged_ptr);
void *aligned_ptr = reinterpret_cast<void *>(
RoundDownTo(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(untagged_ptr), kShadowAlignment));
tag_t pointer_tag = GetTagFromPointer(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tagged_ptr));
Metadata *meta =
reinterpret_cast<Metadata *>(allocator.GetMetaData(aligned_ptr));
if (!meta) {
ReportInvalidFree(stack, reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tagged_ptr));
return;
}
uptr orig_size = meta->GetRequestedSize();
u32 free_context_id = StackDepotPut(*stack);
u32 alloc_context_id = meta->GetAllocStackId();
u32 alloc_thread_id = meta->GetAllocThreadId();
bool in_taggable_region =
InTaggableRegion(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tagged_ptr));
// Check tail magic.
uptr tagged_size = TaggedSize(orig_size);
if (flags()->free_checks_tail_magic && orig_size &&
tagged_size != orig_size) {
uptr tail_size = tagged_size - orig_size - 1;
CHECK_LT(tail_size, kShadowAlignment);
void *tail_beg = reinterpret_cast<void *>(
reinterpret_cast<uptr>(aligned_ptr) + orig_size);
tag_t short_granule_memtag = *(reinterpret_cast<tag_t *>(
reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tail_beg) + tail_size));
if (tail_size &&
(internal_memcmp(tail_beg, tail_magic, tail_size) ||
(in_taggable_region && pointer_tag != short_granule_memtag)))
ReportTailOverwritten(stack, reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tagged_ptr),
orig_size, tail_magic);
}
// TODO(kstoimenov): consider meta->SetUnallocated(free_context_id).
meta->SetUnallocated();
// This memory will not be reused by anyone else, so we are free to keep it
// poisoned.
Thread *t = GetCurrentThread();
if (flags()->max_free_fill_size > 0) {
uptr fill_size =
Min(TaggedSize(orig_size), (uptr)flags()->max_free_fill_size);
internal_memset(aligned_ptr, flags()->free_fill_byte, fill_size);
}
if (in_taggable_region && flags()->tag_in_free && malloc_bisect(stack, 0) &&
atomic_load_relaxed(&hwasan_allocator_tagging_enabled) &&
allocator.FromPrimary(untagged_ptr) /* Secondary 0-tag and unmap.*/) {
// Always store full 8-bit tags on free to maximize UAF detection.
tag_t tag;
if (t) {
// Make sure we are not using a short granule tag as a poison tag. This
// would make us attempt to read the memory on a UaF.
// The tag can be zero if tagging is disabled on this thread.
do {
tag = t->GenerateRandomTag(/*num_bits=*/8);
} while (
UNLIKELY((tag < kShadowAlignment || tag == pointer_tag) && tag != 0));
} else {
static_assert(kFallbackFreeTag >= kShadowAlignment,
"fallback tag must not be a short granule tag.");
tag = kFallbackFreeTag;
}
TagMemoryAligned(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(aligned_ptr), TaggedSize(orig_size),
tag);
}
if (t) {
allocator.Deallocate(t->allocator_cache(), aligned_ptr);
// 这是唯一往Thread::heap_allocations()里push数据的地方。也就是说Thread::heap_allocations()里记录的都是
// 成对的分配
if (auto *ha = t->heap_allocations())
ha->push({reinterpret_cast<uptr>(tagged_ptr), alloc_thread_id,
alloc_context_id, free_context_id,
static_cast<u32>(orig_size)});
} else {
SpinMutexLock l(&fallback_mutex);
AllocatorCache *cache = &fallback_allocator_cache;
allocator.Deallocate(cache, aligned_ptr);
}
}
重点:
每次成对的分配/释放,会以数据结构HeapAllocationRecord的形式保存在Thread::heap_allocations_成员中。
问题Report
问题上报是hwasan中很关键的逻辑,这直接决定我们如何理解hwasan报错,以及如何分析问题。
hwasan报错分为以下几类:
-
InvalidFreeReport
-
TailOverwrittenReport
-
TagMismatchReport(最常见)
我们先看最常见的TagMismatchReport的整个调用链:
HandleTagMismatch hwasan.cpp
ReportTagMismatch // 构造TagMismatchReport对象,之后在其析构函数中执行上报逻辑
TagMismatchReport::TagMismatchReport
BaseReport::BaseReport // 调用父类的构造函数
// 以下是BaseReport构造过程中的关键函数,这些函数会保存各类重要的数据,包括堆、栈的分配等
UntagAddr // 保存一份不含tag的ptr
GetTagFromPointer // 获取ptr tag
FindMismatchOffset
CopyHeapChunk // 拷贝ptr指向的附近user内存的值
CopyAllocations // 拷贝ptr指向内存的分配记录(如果有)
FindBufferOverflowCandidate // 寻找overflow原本访问的内存
CopyShadow // 拷贝ptr指向的附近影子内存的值
TagMismatchReport::~TagMismatchReport //执行上报逻辑
PrintAddressDescription // 输出报错类型
PrintTags
ReportErrorSummary接下来分步骤看整个过程。
TagMismatchReport构造过程
很重要,很多变量都是在此时初始化:
class BaseReport {
public:
/**
* stack: 报错栈
* tagged_addr: 报错地址
*/
BaseReport(StackTrace *stack, bool fatal, uptr tagged_addr, uptr access_size)
: scoped_report(fatal),
stack(stack),
tagged_addr(tagged_addr),
access_size(access_size),
untagged_addr(UntagAddr(tagged_addr)),
ptr_tag(GetTagFromPointer(tagged_addr)),
mismatch_offset(FindMismatchOffset()),
heap(CopyHeapChunk()),
allocations(CopyAllocations()),
candidate(FindBufferOverflowCandidate()),
shadow(CopyShadow()) {}拷贝堆、栈分配记录
TagMismatchReport构造过程
很重要,很多变量都是在此时初始化:
class BaseReport {
public:
/**
* stack: 报错栈
* tagged_addr: 报错地址
*/
BaseReport(StackTrace *stack, bool fatal, uptr tagged_addr, uptr access_size)
: scoped_report(fatal),
stack(stack),
tagged_addr(tagged_addr),
access_size(access_size),
untagged_addr(UntagAddr(tagged_addr)),
ptr_tag(GetTagFromPointer(tagged_addr)),
mismatch_offset(FindMismatchOffset()),
heap(CopyHeapChunk()),
allocations(CopyAllocations()),
candidate(FindBufferOverflowCandidate()),
shadow(CopyShadow()) {}拷贝堆、栈分配记录
BaseReport::Allocations BaseReport::CopyAllocations() {
if (MemIsShadow(untagged_addr))
return {};
uptr stack_allocations_count = 0;
uptr heap_allocations_count = 0;
hwasanThreadList().VisitAllLiveThreads([&](Thread *t) {
if (stack_allocations_count < ARRAY_SIZE(stack_allocations_storage) &&
t->AddrIsInStack(untagged_addr)) {
stack_allocations_storage[stack_allocations_count++].CopyFrom(t);
}
if (heap_allocations_count < ARRAY_SIZE(heap_allocations_storage)) {
// Scan all threads' ring buffers to find if it's a heap-use-after-free.
HeapAllocationRecord har;
uptr ring_index, num_matching_addrs, num_matching_addrs_4b;
if (FindHeapAllocation(t->heap_allocations(), tagged_addr, &har,
&ring_index, &num_matching_addrs,
&num_matching_addrs_4b)) {
//在某个线程找到了对应的分配。注意这个分配是一定包含了释放的,可看“堆分配记录”一节
auto &ha = heap_allocations_storage[heap_allocations_count++];
ha.har = har;
ha.ring_index = ring_index;
ha.num_matching_addrs = num_matching_addrs;
ha.num_matching_addrs_4b = num_matching_addrs_4b;
ha.free_thread_id = t->unique_id();
}
}
});
return {{stack_allocations_storage, stack_allocations_count},
{heap_allocations_storage, heap_allocations_count}};
}寻找可能的溢出访问的buffer
FindBufferOverflowCandidate实现:
BaseReport::OverflowCandidate BaseReport::FindBufferOverflowCandidate() const {
OverflowCandidate result = {};
if (MemIsShadow(untagged_addr))
return result;
// Check if this looks like a heap buffer overflow by scanning
// the shadow left and right and looking for the first adjacent
// object with a different memory tag. If that tag matches ptr_tag,
// check the allocator if it has a live chunk there.
tag_t *tag_ptr = reinterpret_cast<tag_t *>(MemToShadow(untagged_addr));
tag_t *candidate_tag_ptr = nullptr, *left = tag_ptr, *right = tag_ptr;
uptr candidate_distance = 0;
从报错地址对应的影子内存开始前后1000字节的范围内找tag能够匹配的内存。实际user内存的查找范围就是16*1000=16000字节,接近4页。
for (; candidate_distance < 1000; candidate_distance++) {
if (MemIsShadow(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(left)) && TagsEqual(ptr_tag, left)) {
candidate_tag_ptr = left;
break;
}
--left;
if (MemIsShadow(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(right)) &&
TagsEqual(ptr_tag, right)) {
candidate_tag_ptr = right;
break;
}
++right;
}
报错地址和能匹配上tag的内存不超过16字节才算is_close。
constexpr auto kCloseCandidateDistance = 1;
result.is_close = candidate_distance <= kCloseCandidateDistance;
result.after = candidate_tag_ptr == left;
result.untagged_addr = ShadowToMem(reinterpret_cast<uptr>(candidate_tag_ptr));
HwasanChunkView chunk = FindHeapChunkByAddress(result.untagged_addr);
if (chunk.IsAllocated()) {
result.heap.is_allocated = true;
result.heap.begin = chunk.Beg();
result.heap.end = chunk.End();
result.heap.thread_id = chunk.GetAllocThreadId();
result.heap.stack_id = chunk.GetAllocStackId();
}
return result;
}这里反映出,现在的hwasan在检测overflow时确实不够严谨。
现在的方法是,从ptr指向内存开始向两边找,如果能在1000字节的影子内存范围内,找到最近的能匹配ptr的内存,就认为是发生了overflow。
但现实中很可能出现一种情况:
-
ptr指向的内存地址A被释放。
-
A被分配给了其它指针。
-
ptr指向内存的16000字节内恰好随机到一个相同tag的内存块。
-
此时再用ptr去访问原内存(且不超过原内存的范围),发现原内存被分配,但tag不一致。于是前后找,找到了那个恰好相同的tag,于是判定为overflow。
但很明显,按照代码逻辑,这应该算是UAF(只不过被free的内存再次被分配),但却被识别为heap overflow。这正是问题SF signalFrameUpdate hwasan UAF问题分析中遇到的情况。这类问题可以称之为“标签重用”问题。
那么这是我们就要问一个问题了:为什么hwasan会这么设计?为什么不能严谨地判断?
尝试查找相关资料,但没能找到。这里我尝试推测一下。
我认为是实现成本的问题。试想,如果要严谨的判断UAF,我们需要哪些信息?我们是不是得知道每次分配的地址、size和tag,然后还要给这次分配记录一个id。这样当用ptr访问内存时,我们才能查到一次分配的信息,进而判断UAF。
但是在一个复杂的程序里,我们不可能把每一次分配都记录下来,因为这个数据量实在是太大了。当然我们可以给每个内存块最多只记录一次分配,但即便如此数据量仍然很大,而且维护这样的数据运行时开销也很大,毕竟每次内存访问都要执行这些判断。
所以我认为这是hwasan设计,也就是标签匹配方案本身的一个折中。它能够在尽可能检测出问题的情况下,保证运行时开销能接受。否则哪些偶现问题更难以解决了。
报错流程
// compiler-rt/lib/hwasan/hwasan_report.cpp
TagMismatchReport::~TagMismatchReport() {
Decorator d;
// TODO: when possible, try to print heap-use-after-free, etc.
const char *bug_type = "tag-mismatch";
uptr pc = GetTopPc(stack);
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Report("ERROR: %s: %s on address %p at pc %p\n", SanitizerToolName, bug_type,
untagged_addr, pc);
Thread *t = GetCurrentThread();
tag_t mem_tag = GetTagCopy(MemToShadow(untagged_addr + mismatch_offset));
Printf("%s", d.Access());
// 输出ptr/mem的tag信息
if (mem_tag && mem_tag < kShadowAlignment) {
// mem_tag小于16,会输出short tag和随机tag
tag_t short_tag =
GetShortTagCopy(MemToShadow(untagged_addr + mismatch_offset));
Printf(
"%s of size %zu at %p tags: %02x/%02x(%02x) (ptr/mem) in thread T%zd\n",
is_store ? "WRITE" : "READ", access_size, untagged_addr, ptr_tag,
mem_tag, short_tag, t->unique_id());
} else {
Printf("%s of size %zu at %p tags: %02x/%02x (ptr/mem) in thread T%zd\n",
is_store ? "WRITE" : "READ", access_size, untagged_addr, ptr_tag,
mem_tag, t->unique_id());
}
if (mismatch_offset)
Printf("Invalid access starting at offset %zu\n", mismatch_offset);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
stack->Print();
//这里输出错误类型,包括UAF,Heap buffer overflow等
PrintAddressDescription();
t->Announce();
PrintTags(untagged_addr + mismatch_offset);
if (registers_frame)
ReportRegisters(registers_frame, pc);
MaybePrintAndroidHelpUrl();
ReportErrorSummary(bug_type, stack);
}
} // namespace// compiler-rt/lib/hwasan/hwasan_report.cpp
void BaseReport::PrintAddressDescription() const {
Decorator d;
int num_descriptions_printed = 0;
// 输出访问内存块的基本信息
// Print some very basic information about the address, if it's a heap.
if (heap.begin) {
Printf(
"%s[%p,%p) is a %s %s heap chunk; "
"size: %zd offset: %zd\n%s",
d.Location(), heap.begin, heap.begin + heap.size,
heap.from_small_heap ? "small" : "large",
heap.is_allocated ? "allocated" : "unallocated", heap.size,
untagged_addr - heap.begin, d.Default());
}
auto announce_by_id = [](u32 thread_id) {
hwasanThreadList().VisitAllLiveThreads([&](Thread *t) {
if (thread_id == t->unique_id())
t->Announce();
});
};
// 输出stack错误。allocations的赋值点就很重要。
// Check stack first. If the address is on the stack of a live thread, we
// know it cannot be a heap / global overflow.
for (const auto &sa : allocations.stack) {
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: stack tag-mismatch\n");
Printf("%s", d.Location());
Printf("Address %p is located in stack of thread T%zd\n", untagged_addr,
sa.thread_id());
Printf("%s", d.Default());
announce_by_id(sa.thread_id());
PrintStackAllocations(sa.get(), ptr_tag, untagged_addr);
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
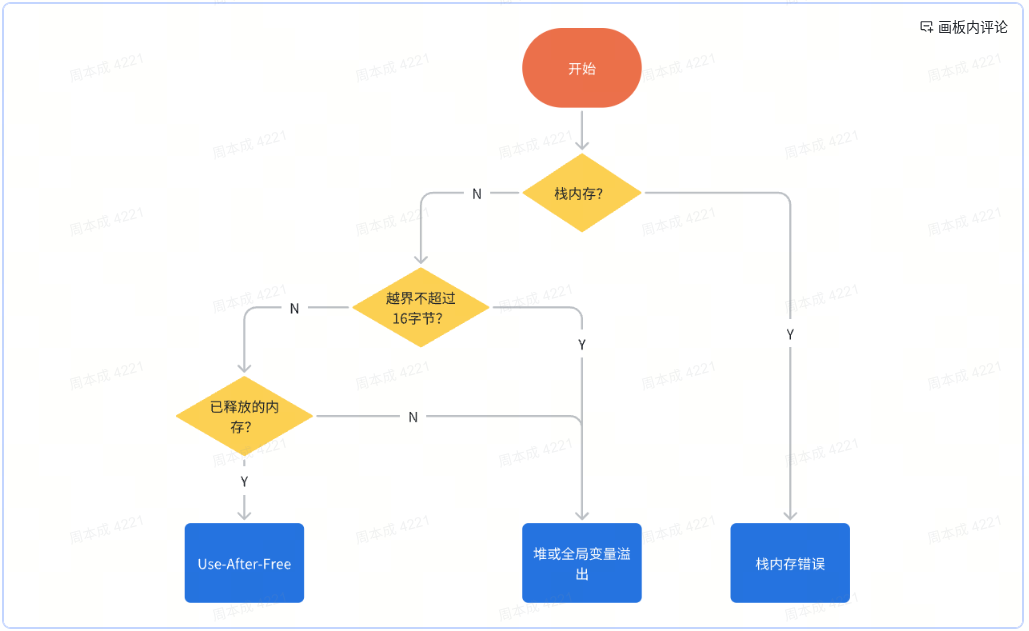
// 满足全部以下条件就是heap-buffer-overflow or global-overflow:
1. allocations.stack为空,说明内存不是栈内存
2. 地址不为0
3. candidate.is_close。
if (allocations.stack.empty() && candidate.untagged_addr &&
candidate.is_close) {
PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate();
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// UAF。上面的if没return,说明overflow和UAF可能同时出现?感觉不合理,实际也没见过。
for (const auto &ha : allocations.heap) {
const HeapAllocationRecord har = ha.har;
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: use-after-free\n");
Printf("%s", d.Location());
Printf("%p is located %zd bytes inside a %zd-byte region [%p,%p)\n",
untagged_addr, untagged_addr - UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr),
har.requested_size, UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr),
UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr) + har.requested_size);
Printf("%s", d.Allocation());
Printf("freed by thread T%u here:\n", ha.free_thread_id);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
GetStackTraceFromId(har.free_context_id).Print();
Printf("%s", d.Allocation());
Printf("previously allocated by thread T%u here:\n", har.alloc_thread_id);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
GetStackTraceFromId(har.alloc_context_id).Print();
// Print a developer note: the index of this heap object
// in the thread's deallocation ring buffer.
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_heap_rb_distance: %zd %zd\n", ha.ring_index + 1,
flags()->heap_history_size);
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_num_matching_addrs: %zd\n", ha.num_matching_addrs);
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_num_matching_addrs_4b: %zd\n",
ha.num_matching_addrs_4b);
announce_by_id(ha.free_thread_id);
// TODO: announce_by_id(har.alloc_thread_id);
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// 这里注意,如果前面两种都没输出,那么还是按照overflow处理
if (candidate.untagged_addr && num_descriptions_printed == 0) {
PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate();
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// Print the remaining threads, as an extra information, 1 line per thread.
if (flags()->print_live_threads_info) {
Printf("\n");
hwasanThreadList().VisitAllLiveThreads([&](Thread *t) { t->Announce(); });
}
if (!num_descriptions_printed)
// We exhausted our possibilities. Bail out.
Printf("HWAddressSanitizer can not describe address in more detail.\n");
if (num_descriptions_printed > 1) {
Printf(
"There are %d potential causes, printed above in order "
"of likeliness.\n",
num_descriptions_printed);
}
}PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate:实现:
// compiler-rt/lib/hwasan/hwasan_report.cpp
void BaseReport::PrintAddressDescription() const {
Decorator d;
int num_descriptions_printed = 0;
// 输出访问内存块的基本信息
// Print some very basic information about the address, if it's a heap.
if (heap.begin) {
Printf(
"%s[%p,%p) is a %s %s heap chunk; "
"size: %zd offset: %zd\n%s",
d.Location(), heap.begin, heap.begin + heap.size,
heap.from_small_heap ? "small" : "large",
heap.is_allocated ? "allocated" : "unallocated", heap.size,
untagged_addr - heap.begin, d.Default());
}
auto announce_by_id = [](u32 thread_id) {
hwasanThreadList().VisitAllLiveThreads([&](Thread *t) {
if (thread_id == t->unique_id())
t->Announce();
});
};
// 输出stack错误。allocations的赋值点就很重要。
// Check stack first. If the address is on the stack of a live thread, we
// know it cannot be a heap / global overflow.
for (const auto &sa : allocations.stack) {
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: stack tag-mismatch\n");
Printf("%s", d.Location());
Printf("Address %p is located in stack of thread T%zd\n", untagged_addr,
sa.thread_id());
Printf("%s", d.Default());
announce_by_id(sa.thread_id());
PrintStackAllocations(sa.get(), ptr_tag, untagged_addr);
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// 满足全部以下条件就是heap-buffer-overflow or global-overflow:
1. allocations.stack为空,说明内存不是栈内存
2. 地址不为0
3. candidate.is_close。
if (allocations.stack.empty() && candidate.untagged_addr &&
candidate.is_close) {
PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate();
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// UAF。上面的if没return,说明overflow和UAF可能同时出现?感觉不合理,实际也没见过。
for (const auto &ha : allocations.heap) {
const HeapAllocationRecord har = ha.har;
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: use-after-free\n");
Printf("%s", d.Location());
Printf("%p is located %zd bytes inside a %zd-byte region [%p,%p)\n",
untagged_addr, untagged_addr - UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr),
har.requested_size, UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr),
UntagAddr(har.tagged_addr) + har.requested_size);
Printf("%s", d.Allocation());
Printf("freed by thread T%u here:\n", ha.free_thread_id);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
GetStackTraceFromId(har.free_context_id).Print();
Printf("%s", d.Allocation());
Printf("previously allocated by thread T%u here:\n", har.alloc_thread_id);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
GetStackTraceFromId(har.alloc_context_id).Print();
// Print a developer note: the index of this heap object
// in the thread's deallocation ring buffer.
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_heap_rb_distance: %zd %zd\n", ha.ring_index + 1,
flags()->heap_history_size);
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_num_matching_addrs: %zd\n", ha.num_matching_addrs);
Printf("hwasan_dev_note_num_matching_addrs_4b: %zd\n",
ha.num_matching_addrs_4b);
announce_by_id(ha.free_thread_id);
// TODO: announce_by_id(har.alloc_thread_id);
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// 这里注意,如果前面两种都没输出,那么还是按照overflow处理
if (candidate.untagged_addr && num_descriptions_printed == 0) {
PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate();
num_descriptions_printed++;
}
// Print the remaining threads, as an extra information, 1 line per thread.
if (flags()->print_live_threads_info) {
Printf("\n");
hwasanThreadList().VisitAllLiveThreads([&](Thread *t) { t->Announce(); });
}
if (!num_descriptions_printed)
// We exhausted our possibilities. Bail out.
Printf("HWAddressSanitizer can not describe address in more detail.\n");
if (num_descriptions_printed > 1) {
Printf(
"There are %d potential causes, printed above in order "
"of likeliness.\n",
num_descriptions_printed);
}
}
PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate实现:
void BaseReport::PrintHeapOrGlobalCandidate() const {
Decorator d;
if (candidate.heap.is_allocated) {
// 内存是堆上分配的,所以认为是heap buffer overflow
uptr offset;
const char *whence;
if (candidate.heap.begin <= untagged_addr &&
untagged_addr < candidate.heap.end) {
offset = untagged_addr - candidate.heap.begin;
whence = "inside";
} else if (candidate.after) {
offset = untagged_addr - candidate.heap.end;
whence = "after";
} else {
offset = candidate.heap.begin - untagged_addr;
whence = "before";
}
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: heap-buffer-overflow\n");
Printf("%s", d.Default());
Printf("%s", d.Location());
Printf("%p is located %zd bytes %s a %zd-byte region [%p,%p)\n",
untagged_addr, offset, whence,
candidate.heap.end - candidate.heap.begin, candidate.heap.begin,
candidate.heap.end);
Printf("%s", d.Allocation());
Printf("allocated by thread T%u here:\n", candidate.heap.thread_id);
Printf("%s", d.Default());
GetStackTraceFromId(candidate.heap.stack_id).Print();
return;
}
// Check whether the address points into a loaded library. If so, this is
// most likely a global variable.
const char *module_name;
uptr module_address;
Symbolizer *sym = Symbolizer::GetOrInit();
if (sym->GetModuleNameAndOffsetForPC(candidate.untagged_addr, &module_name,
&module_address)) {
Printf("%s", d.Error());
Printf("\nCause: global-overflow\n");
Printf("%s", d.Default());
DataInfo info;
Printf("%s", d.Location());
if (sym->SymbolizeData(candidate.untagged_addr, &info) && info.start) {
Printf(
"%p is located %zd bytes %s a %zd-byte global variable "
"%s [%p,%p) in %s\n",
untagged_addr,
candidate.after ? untagged_addr - (info.start + info.size)
: info.start - untagged_addr,
candidate.after ? "after" : "before", info.size, info.name,
info.start, info.start + info.size, module_name);
} else {
uptr size = GetGlobalSizeFromDescriptor(candidate.untagged_addr);
if (size == 0)
// We couldn't find the size of the global from the descriptors.
Printf(
"%p is located %s a global variable in "
"\n #0 0x%x (%s+0x%x)\n",
untagged_addr, candidate.after ? "after" : "before",
candidate.untagged_addr, module_name, module_address);
else
Printf(
"%p is located %s a %zd-byte global variable in "
"\n #0 0x%x (%s+0x%x)\n",
untagged_addr, candidate.after ? "after" : "before", size,
candidate.untagged_addr, module_name, module_address);
}
Printf("%s", d.Default());
}
}
小结
UAF和overflow的判断逻辑
根据代码做进一步的提炼,总体逻辑如下: